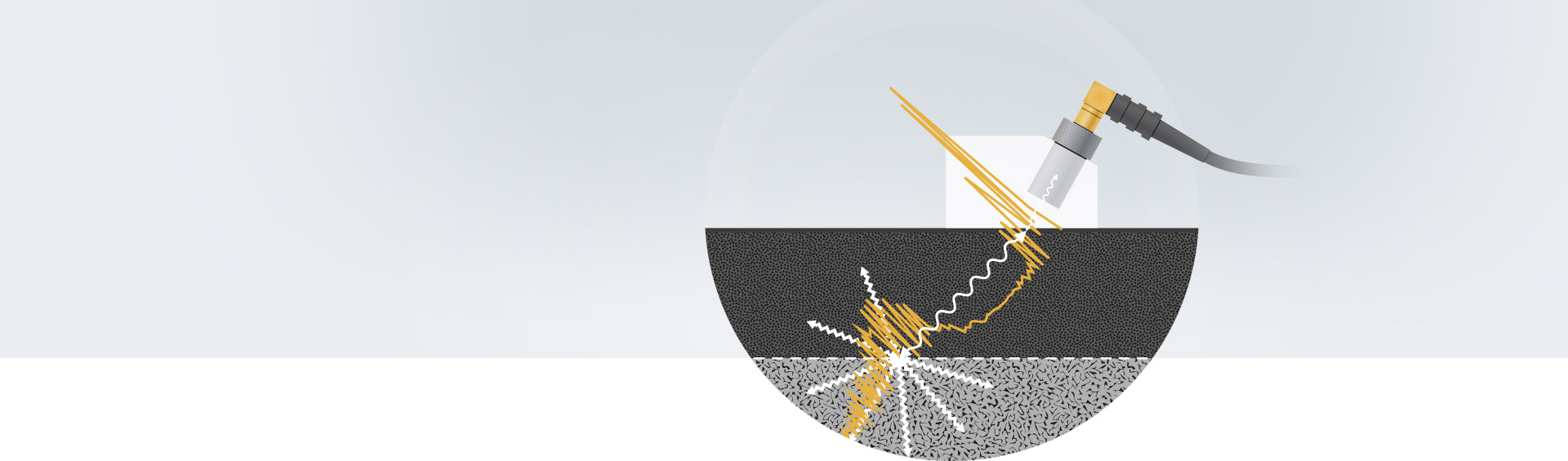
Ultrasonic waves propagating in polycrystalline materials (steel) are scattered at material interfaces with changes of density and/or elastic properties. In general, the ultrasonic waves are scattered in all directions, partly also back to the ultrasonic transducer that generated the ultrasonic pulse. The intensity of backscattered ultrasound received by the transducer depends on the ratio of the geometric size of the scattering geometry to the wavelength of the ultrasound and on the degree of material property difference at the interface denoted by the term acoustic impedance change.
In the area where the ultrasonic wave length is large compared to the size of the scattering geometry, higher ultrasound frequencies (or shorter wave lengths) increase the intensity of ultrasonic backscattering. Furthermore, the intensity of backscattering increases with the average effective size of the scattering geometry, for example the grain size of the polycrystalline steel. Using the appropriate frequency of about 20 MHz, the microstructure change between the hardened case (usually fine-grained Martensite) and the core material with coarse-grained microstructure causes a distinct increase of backscattering intensity. This effect can be observed when the ultrasonic pulse crosses the interface and standard time of flight evaluation yields the depth position of the interface that corresponds to the Surface Hardening Depth (SHD) (see figure 1).
Contact:
Dipl.-Ing. Tobias Müller
Phone: + 49 (0) 681/9767153
Fax: + 49 (0) 681/9767158
From the time it takes for the sound pulse to travel from the surface of the part to the place at which the scattering is caused, the thickness of the hardened zone can be calculated via the known sound velocity of the material.
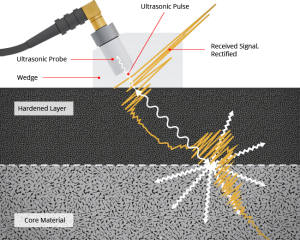
Figure 1: The Ultrasonic Backscatter Technique (UBT)
Ultrasonic SHD testing is based on completely different physical principles compared to metallographic methods, such as microhardening testing or other destructive methods. Therefore, SHD values obtained with the UBT are not necessarily identical to destructive SHD values. Nevertheless, in most cases there is a good correlation between the two values, because both methods are influenced by the hardness process, particularly the location of the interface between hardened case to core material .
Conditions
parts are flame, laser or induction hardened
parts are forged, not cast
the minimum SHD value is higher than ~ 1.2 mm
there is a distinct interface between hardened material and core material
backscattering within the base material is of sufficiently high intensity for ultrasonic frequencies of 20 MHz